Artificial Intelligence Dual-Stain Approach Improved Accuracy, Efficiency of Cervical Cancer Screening
, by NCI press release
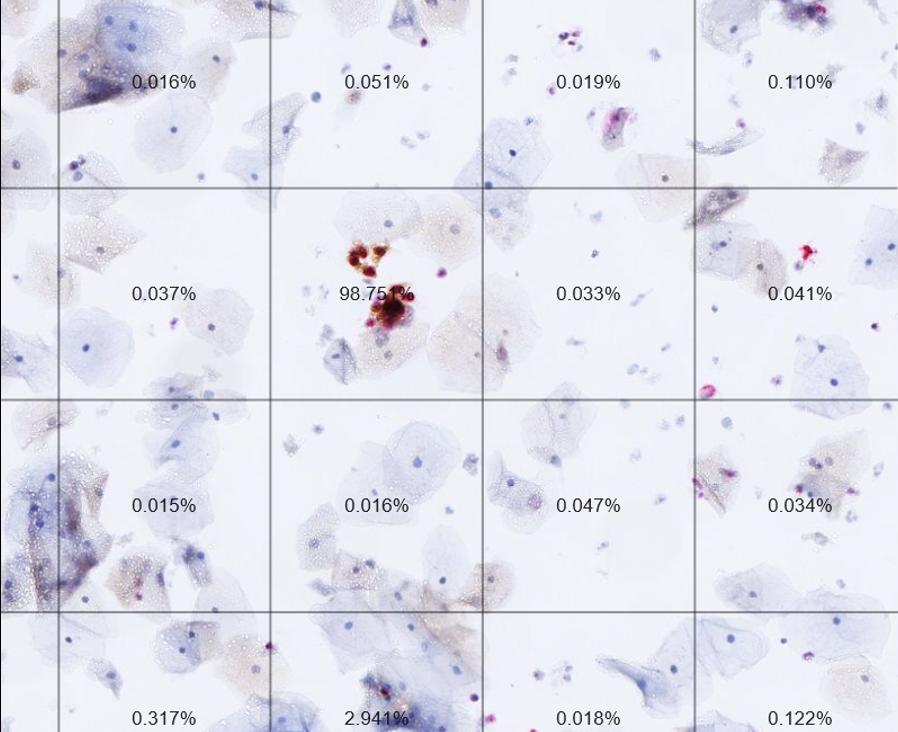
In a new study, a computer algorithm improved the accuracy and efficiency of cervical cancer screening compared with cytology (Pap test), the current standard for follow-up of women who test positive with primary human papillomavirus (HPV) screening. The new approach uses artificial intelligence (AI) to automate dual-stain evaluation and has clear implications for clinical care.
Findings from the study were published June 25, 2020, in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute. The algorithm was developed and the study conducted by investigators at the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health, in collaboration with researchers from several other institutions.
"We're excited to show we have a fully automated approach to cervical cancer screening as a follow-up to a positive HPV test that outperformed the standard method in our study," said Nicolas Wentzensen, M.D., Ph.D., of NCI's Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, who led the study. "Based on our results, it could increase the efficiency of cervical cancer screening by finding more precancers and reducing false positives, which has the potential to eliminate a substantial number of unnecessary procedures among HPV-positive women."
Read the complete NCI press release.
Wentzensen N, et al. Accuracy and Efficiency of Deep-Learning-Based Automation of Dual Stain Cytology in Cervical Cancer Screening. J Natl Cancer Inst. June 25, 2020. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djaa066