First Direct Comparison of Screening Methods for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
, by Jennifer K. Loukissas, M.P.P.
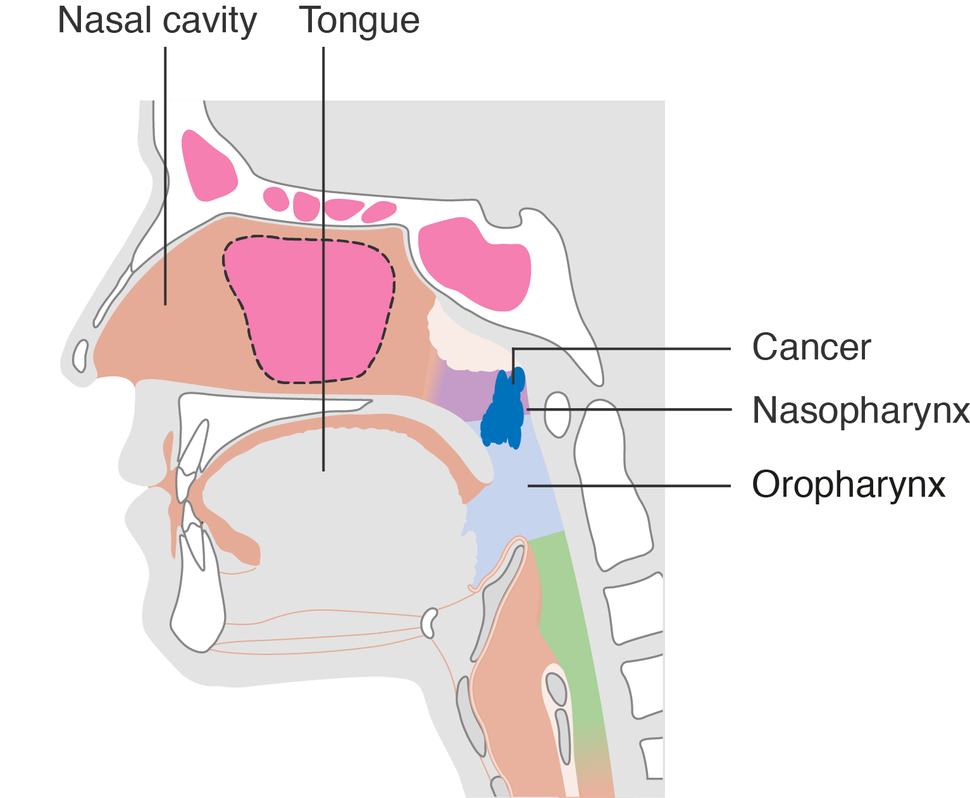
Investigators in the Infections and Immunoepidemiology Branch, led by Zhiwei Liu, Ph.D., tenure track investigator, compared two approaches to screen for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in blood for early detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC): antibody- and DNA-based approaches. Their findings were published July 21, 2023, in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The two approaches were shown to be effective but had not previously been validated: an EBV antibody score using immunoglobulin A antibodies measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and plasma EBV DNA load measured by real-time PCR followed by next-generation sequencing among EBV DNA–positive individuals. The investigators compared their performance in an independent population of 819 incident Taiwanese NPC cases diagnosed from 2010 to 2014 and 1,768 controls from the same region and matched on age and sex.
The authors noted, “high sensitivity and specificity of both approaches in distinguishing NPC cases from noncases, underscoring the promise of both approaches for NPC detection. The EBV antibody–based score had slightly inferior performance compared with the EBV DNA–based algorithm, with a slightly lower sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value.”
This new analysis provides important confirmation of their performance and outlines the need to assess the cost-effectiveness of these two methods.
Reference
Lou P-J et al. Performance and operational feasibility of Epstein-Barr virus–based screening for detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Direct comparison of two alternative approaches. J Clin Oncol. 2023.