Advances in Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging and the increasing number of radiopharmaceuticals have resulted in a surge of diagnostic nuclear medicine applications. Therapeutic applications are also gaining ground because of the possibility of systemic, targeted treatments. NCINM, the National Cancer Institute dosimetry system for Nuclear Medicine, has been developed to provide accurate dosimetry for patients undergoing nuclear medicine procedures1-2.
State-of-the-art Phantoms
Most of the current dosimetry tools for nuclear medicine procedures are based on simplified phantoms developed in the 1970s or the ones not representing reference human anatomy. NCINM incorporates state-of-the-art pediatric and adult computational human phantoms, including the hybrid phantom series developed in collaboration between the University of Florida and the National Cancer Institute3 and the reference pediatric and adult phantom series reported by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP)4-5. Implementing additional non-human phantoms representing mice, canines, and primates is in progress.
Comprehensive Dosimetry Database
NCINM includes a comprehensive library of dose conversion coefficients for various radionuclides, called S values, which convert cumulated activities in source regions to absorbed doses in target regions. The program covers up to 68 source regions and 55 target regions defined within the human anatomy. S values are available for a total of 300 clinically-relevant radionuclides for which energy spectra were obtained from the ICRP Publication 107.
Up-to-date Biokinetic Data
A comprehensive library of biokinetic data for over 200 radiopharmaceuticals was collected from a series of ICRP Publications 53, 62, 80, and 128 and implemented into NCINM after adjusting them to match the anatomical definition of modern computational human phantoms. Users can select a radiopharmaceutical in the NCINM user interface, and corresponding biokinetic data will be automatically populated in the source regions of a given phantom.
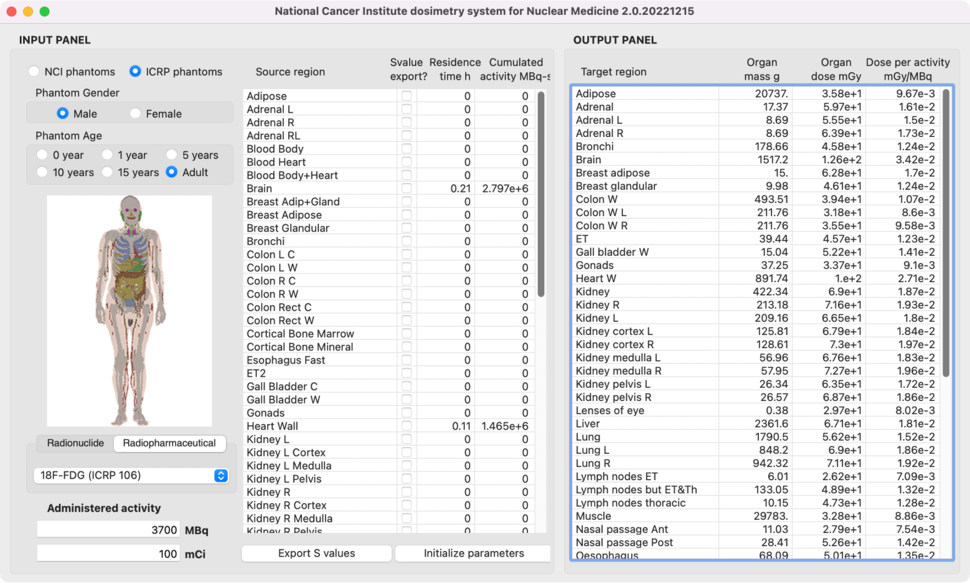
Intuitive User Interface
NCINM provides an intuitive graphical user interface allowing users to select from various computational human phantoms, enter the radionuclide or radiopharmaceutical and its administered activity, and organ residence times. NCINM rapidly calculates the organ dose and dose per administered activity using the pre-calculated database. All input and output processes are conducted in a single interface. NCINM runs on multiple platforms, including Windows, Mac, and LINUX.
How to Access This Resource
Non-Commercial Research Use
There is no charge to use these resources for non-commercial research purposes. Please click Software Transfer Agreement form, fill out the form in your web browser*, save it to your computer, then obtain the signatures and submit it to Dr. Choonsik Lee.
*Browsers tested with the form: Safari, Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, and Firefox.
Commercial Use
Contact Dr. Kevin Chang of the NCI Technology Transfer Center to discuss accessing free trials and the licensing process for commercial use.